Weaving Glossary
With the appeal for fast fashion and the need for quick and cheap fabric still on a sustained rise, the demand for automated processes has become higher than ever. As such, the automated loom has become a ubiquitous part of society. A high-performing loom has the potential of weaving over 1,000 weft threads per minute.
However, the automated loom only grazes the surface of weaving history, there is a rich history of the manual (non-automated) loom. All these looms have certain tools and parts in common; the essentials needed to weave fabric.
This week we will review these essential parts with simple definitions and imagery. With this knowledge, any basic loom/weave structure can be understood.
Many of the definitions this week are paraphrased from Anni Albers On Weaving. Her writings were the first of their kind, elevating the field of weaving beyond technical and into the theoretical.
Weaving / Woven
The processing of creating fabric, composed two sets of thread, warp and weft, sitting perpendicular to each other. These threads move through a series of over / under motions which create interlacing bonds. There is opportunity for these interlacings to create patterns that are either/both structural and decorative.
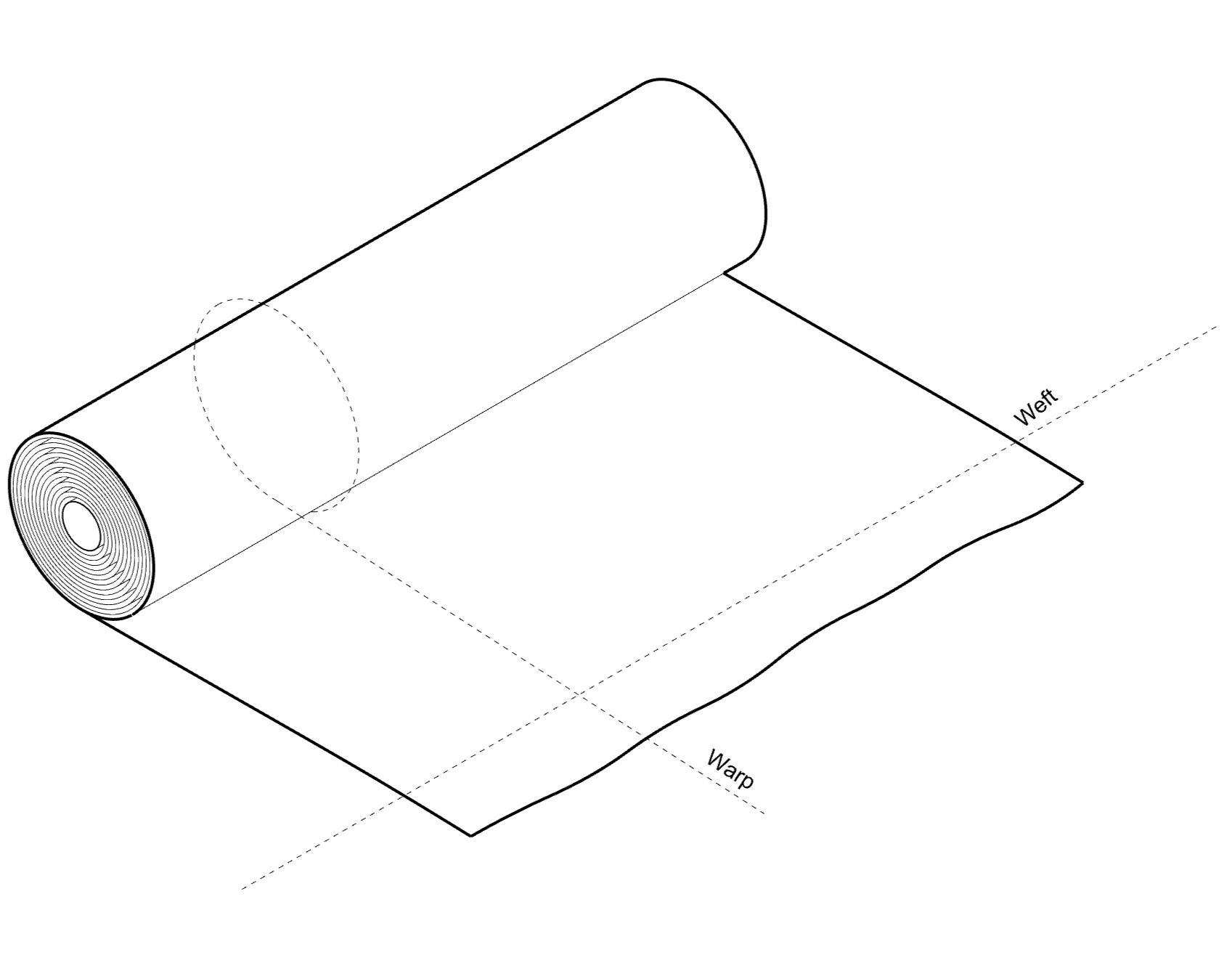
Warp
In all woven fabrics, there is a set of yarns running lengthwise, sitting parallel and at equal tension. The length of warp is dependent on user discrepancy. The warp is the base of fabrics potential. Alternative Name: End
Weft
In all woven fabrics, the weft runs perpendicular to the warp. Each thread individually inserted either manually or by machine. Alternative Name: Filling, Woof, Pick
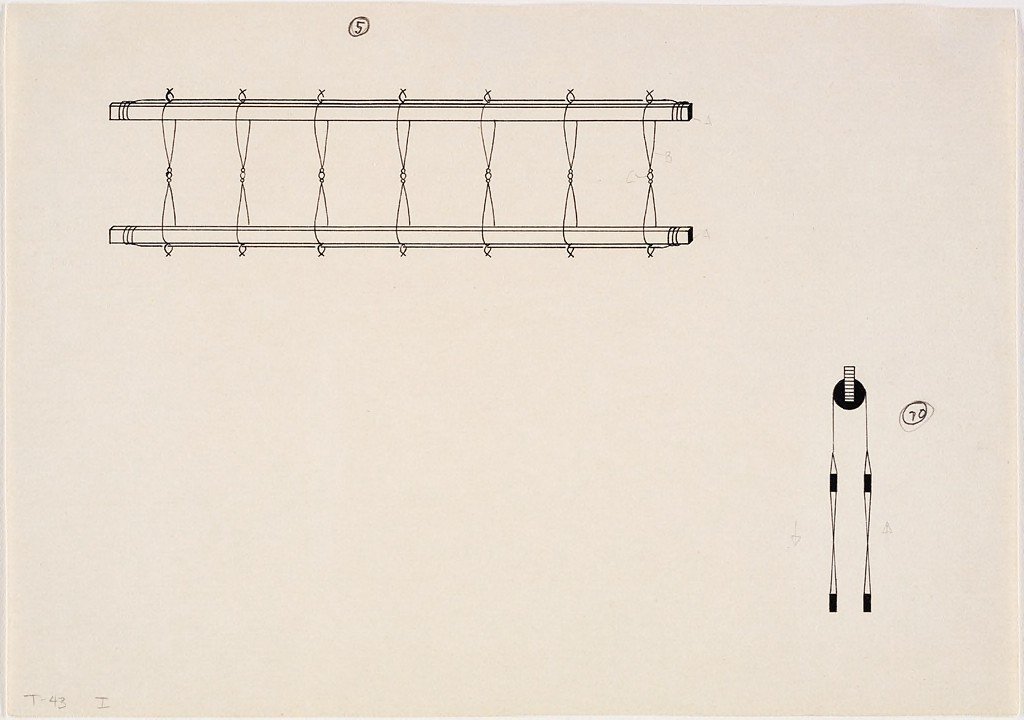
Heddle
A thin piece of metal or bonded nylon, the heddle has three loops: the outer loops attach to the loom, the inner loop holds a warp end. It controls and lifts the warp ends evenly. Alternative Name: Shaft, Frame
Harness
A frame inside a loom. Heddles are connected to a harness, so when a harness is lifted, so are the warp ends. This allows many warp ends to be lifted at once. Once warp ends have been place on heddles/harness they cannot be changed mid weaving. Alternative Names: Shaft, Frame
Reed
Resembling a comb, the reed sets the density of thread. The spacings or slats of the reed are called dents. Individual warp ends are threaded through the dents as the last step before weaving. The strength and stability of the reed is also used to “pack” or “beat” fabric while weaving. In two harness looms, the heddles and reed are combined and called rigid heddles.
Dressing
Dressing the loom is the process of setting up the warp in preparation of weaving. This included attaching the warp, threading the heddles and reed.
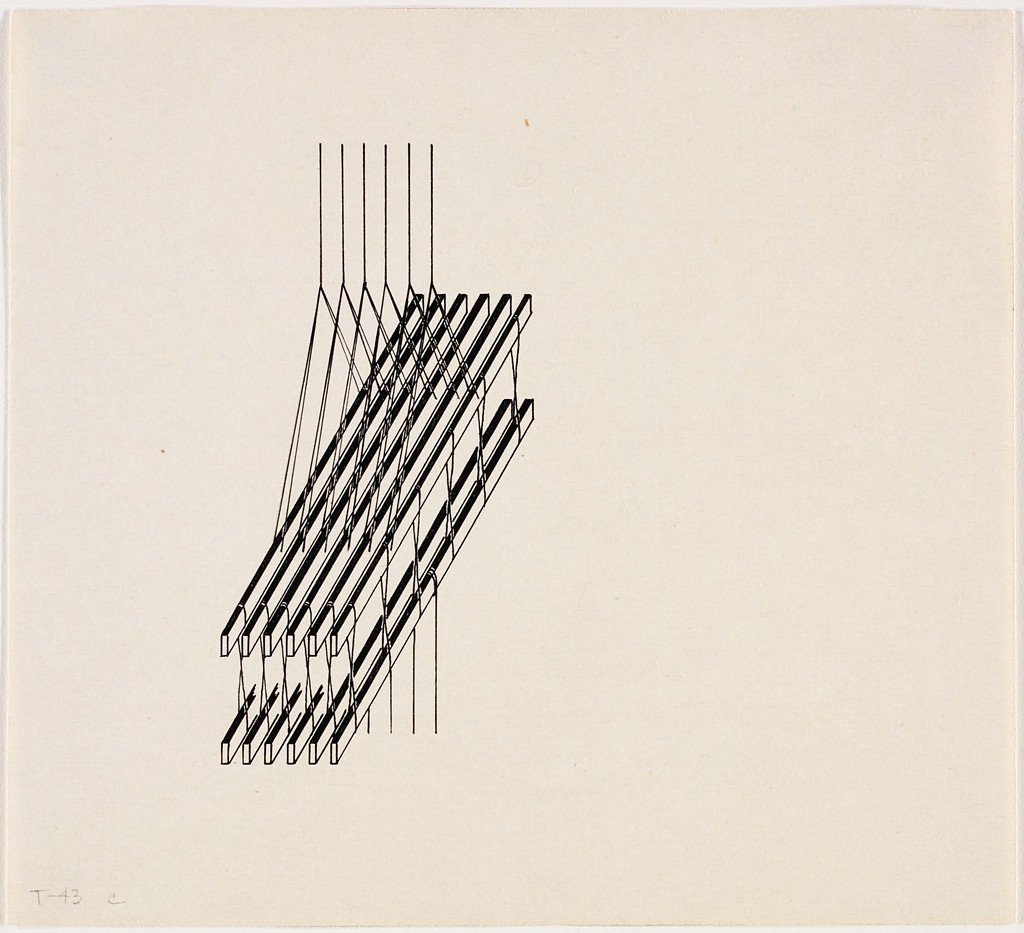
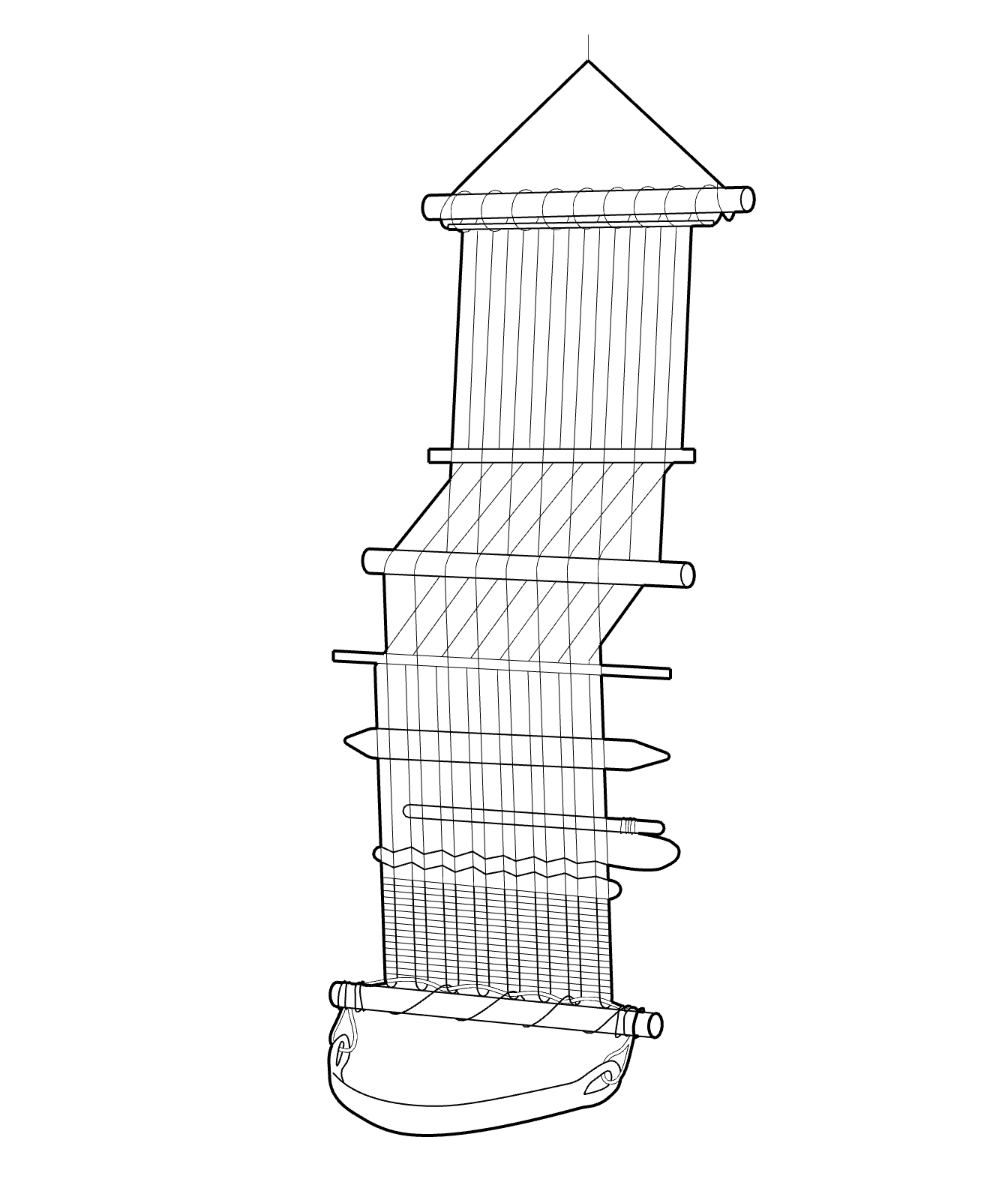
Shuttle Drawing by Lina Bergner, 1943
Shuttle
A tool used during the weaving process; it carries the weft thread from one side of the warp to another. Shaped like a boat, each side is tapered to allow for smooth action. When performed manually, the shuttle is hand pushed across the warp, this action is often termed “throwing” across the loom. Alternative Names: Boat, Rapier Arm, Flying Shuttle
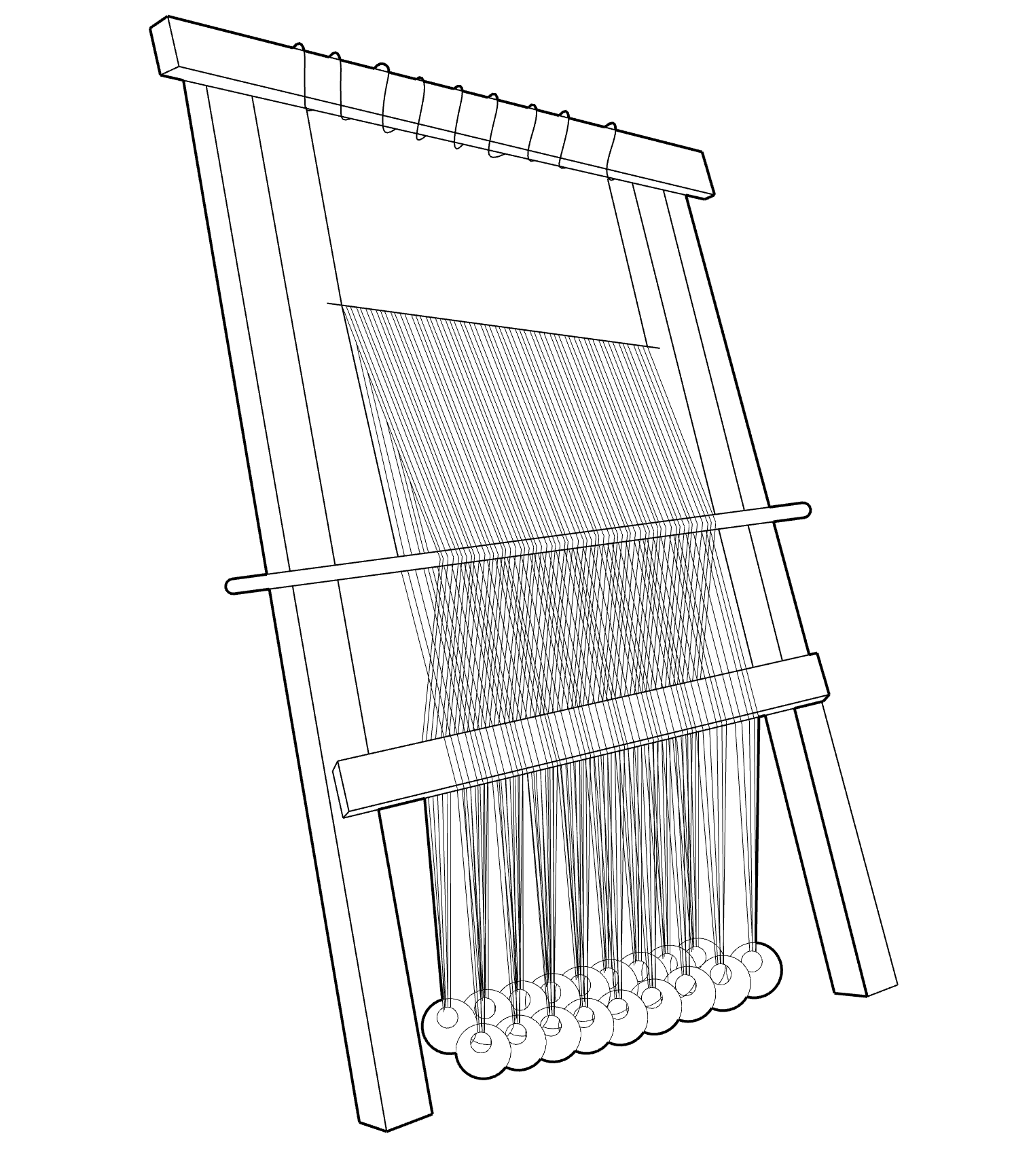
Warp-weighted Loom
The warp is suspended from an upper bar and weighted and the bottom. Unlike other weaving processes, the woven material progresses downwards. It was used in ancient Greece, and more recently by Indians of the North Pacific American coast.
Backstrap Loom
The warp is stretched from bar to bar or wound onto a back bar. Used either vertically or horizontally, the warp was held taut by a framework or stakes in the ground. Early depictions of Egyptian weaving are show using this type of loom in the vertical position. Today, this can be translated to a tapestry loom.
Two-Bar Loom
Lower bar is attached to a belt around the waist of the weaver, who, leaning forward or backward can tighten or slacken the warp. This loom is most notably used in pre-Columbian Peru.
References:
Albers, Anni. On Weaving, Expanded Edition (Princeton University Press, 2017)
Images:
Harvard Art Museum, Special Archival Collection.